High-Purity Materials in Semiconductors
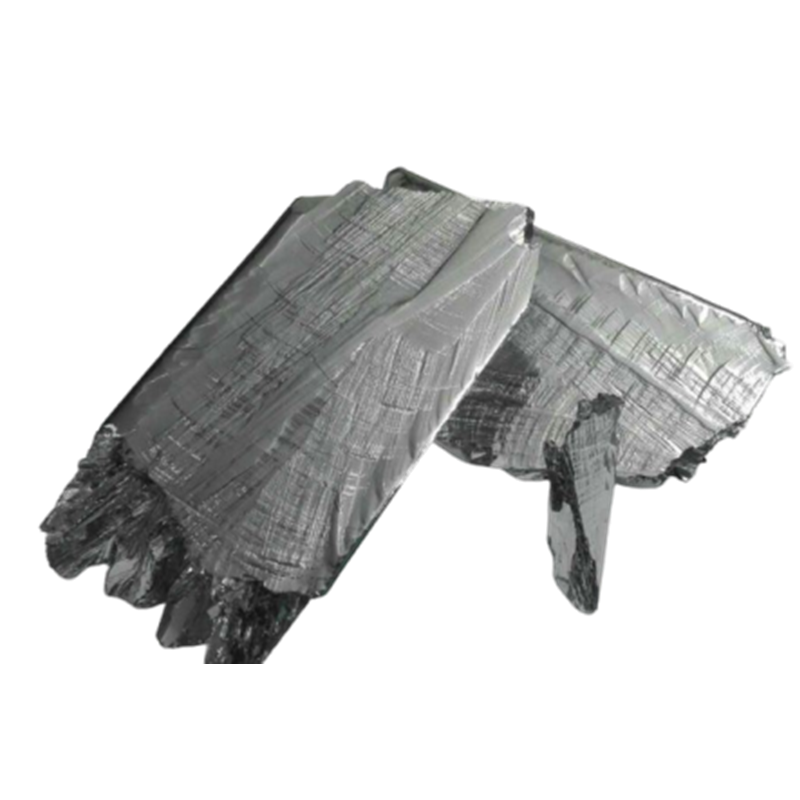

7N Tellurium
Tellurium is a metalloid element, with the element symbol Te, belonging to the VIA group in the periodic table, atomic number 52, atomic mass 127.6. Tellurium has a melting point of 452°C and a boiling point of 1390°C.
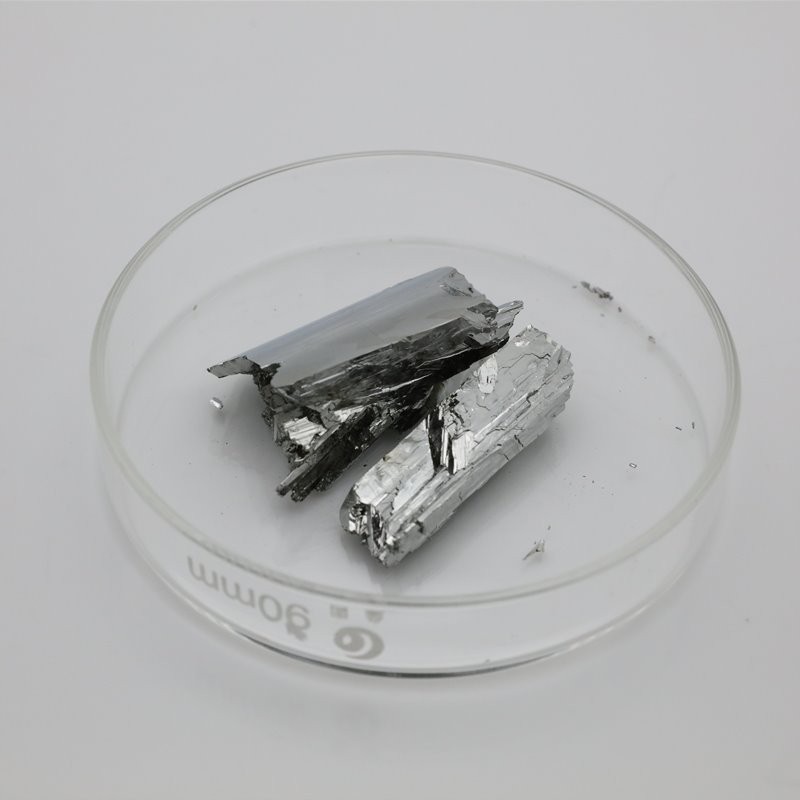

6N Tellurium
Tellurium is a chemical element with the symbol Te and atomic number 52. It is a brittle, mildly toxic, rare, silver-white metalloid. Tellurium is chemically related to selenium and sulfur, all three of which are chalcogens.
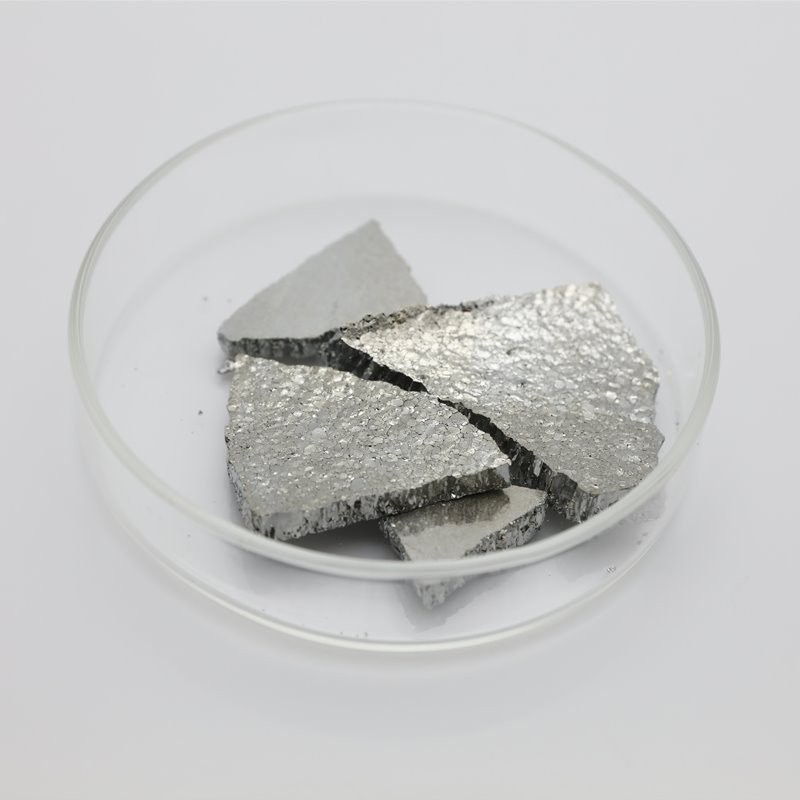

5N Tellurium
Tellurium is a semimetallic, lustrous, crystalline, brittle, silver-white element. It is usually available as a dark grey powder, it has the properties both of the metals and the non metals. Tellurium forms many compounds corresponding to those of sulfur and selenium.
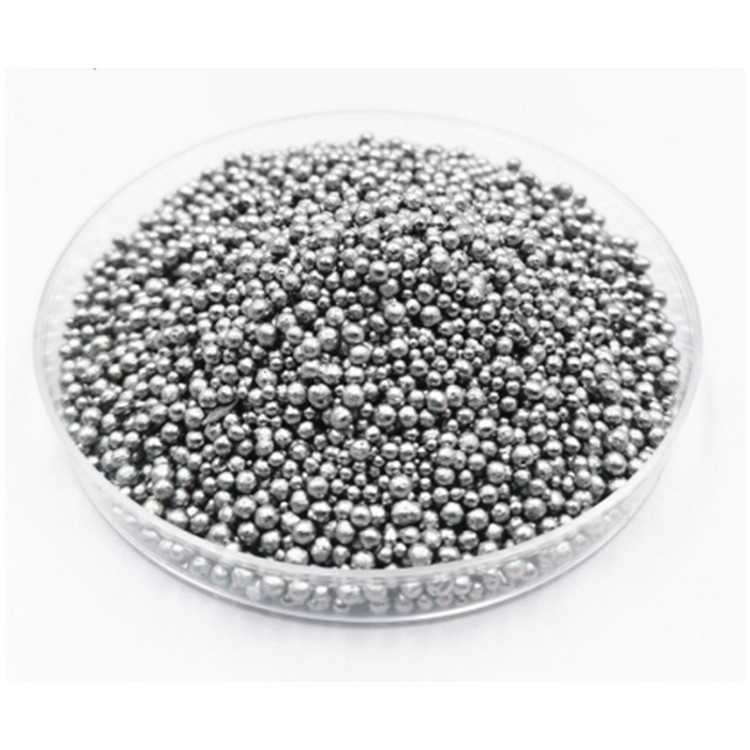

4N Tellurium
Tellurium (Te), semimetallic chemical element in the oxygen group (Group 16 [VIa] of the periodic table), closely allied with the element selenium in chemical and physical properties.

7N5 Indium
The element symbol of indium is In, atomic number 49, atomic weight 114.8, silver-white metal, ductile, melting point 156.61 ℃, boiling point 2080 ℃, hardness 1.2, density 7.30g/c㎡.

7N Indium
Indium is a silver gray, extremely soft, fusible metal. Melting point 156.61 ℃. Boiling point: 2060 ℃. Relative density d7.30.

6N5 Indium
Indium is a silver gray, extremely soft, fusible metal. Melting point 156.61 ℃. Boiling point: 2060 ℃. Relative density d7.30.

6N Indium
Indium is a silver gray, extremely soft, fusible metal. Melting point 156.61 ℃. Boiling point: 2060 ℃. Relative density d7.30. Liquid indium can infiltrate the glass, and will adhere to the contacted surface, leaving black marks.

5N Indium
Indium is a silver gray, extremely soft, fusible metal. Melting point 156.61 ℃. Boiling point: 2060 ℃. Relative density d7.30. Liquid indium can infiltrate the glass, and will adhere to the contacted surface, leaving traces of chemicalbook black.

4N Indium
The element symbol of indium is In, atomic number 49, atomic weight 114.8, silver-white metal, ductile, melting point 156.61 ℃, boiling point 2080 ℃, hardness 1.2, density 7.30g/c㎡.

7N Gallium
Gallium is a soft silvery metal and is a brittle solid at low temperature. It will melt into liquid when room temperature exceeds 29.8 °C(85.57 °F).

6N Gallium
Gallium does not dissolve in water, soluble in acid, alkali, react with sulfur, selenium, tellurium, phosphorus, arsenic and antimony at high temperature.

4N Gallium
Gallium is a metalloid element, with the element symbol Ga, belonging to the VIA group in the periodic table, atomic number 31, atomic mass 69.723.
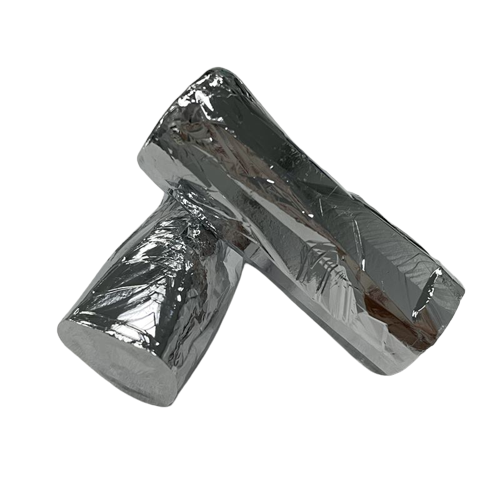

7N5 Cadmium
Cadmium symbol is Cd, atomic number is 48, found in 1817, the element is silver white metal. It's an excellent metal that absorbs neutrons.
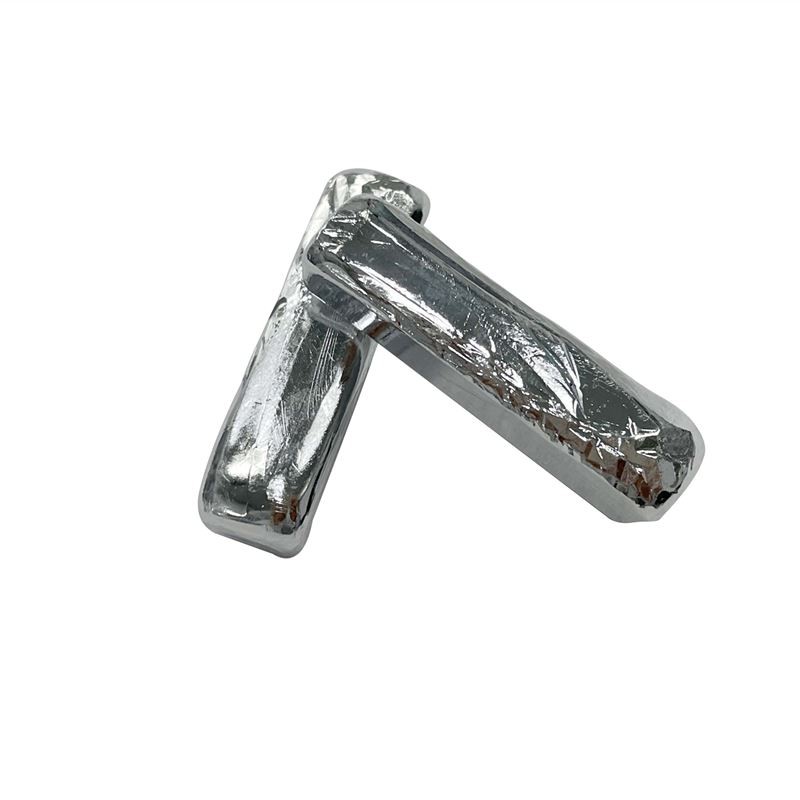

7N Cadmium
Cadmium is one silver-white glossy metal with ductility and toughness, melting point is 320.9℃, density is 8650kg/m³.
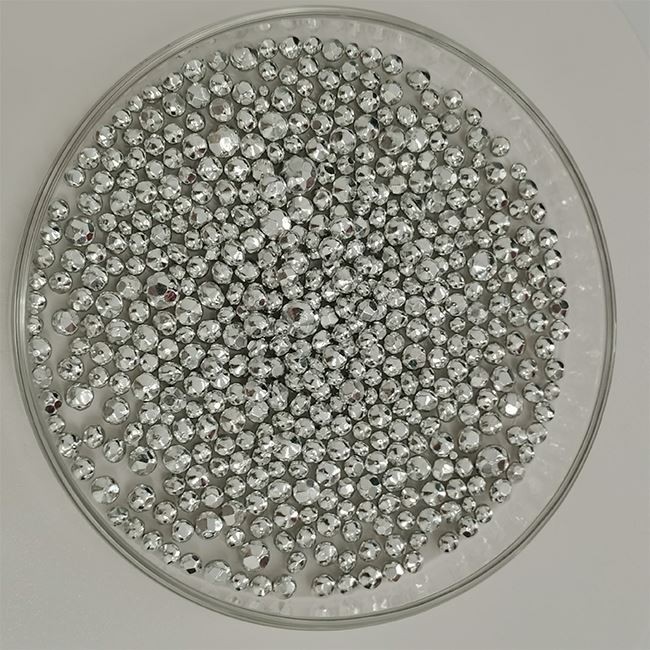

6N Cadmium
Cadmium is one silver-white glossy metal with ductility and toughness, melting point is 320.9℃, density is 8650kg/m³. The ratio of material and Cadmium in the earth is 1000000: 0.1~1000000: 0.5.
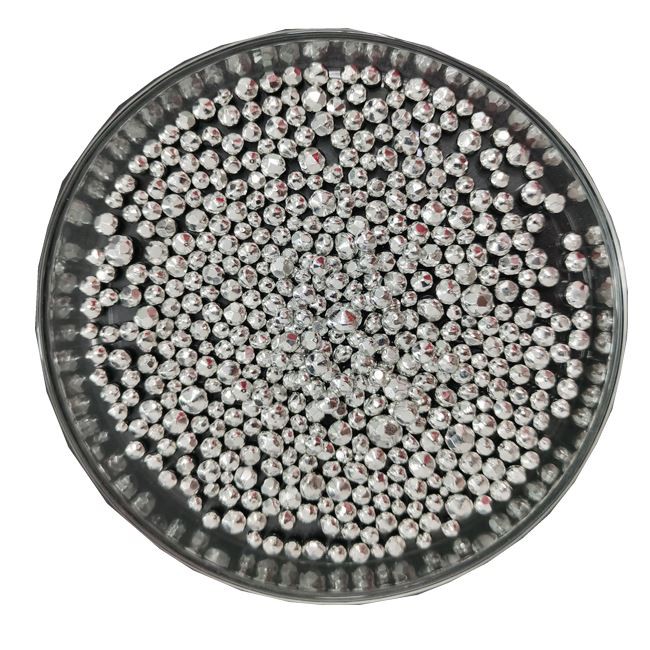

5N Cadmium
Cadmium is one silver-white glossy metal with ductility and toughness, melting point is 320.9℃, density is 8650kg/m³.

4N Cadmium
Cadmium is one silver-white glossy metal. The main application field is for battery, in the nickel-cadmium battery.

7N5 Antimony
Antimony is one metal element, with symbol of Sb, atomic number is 51, is silver white glossy hard and fragile metal. (commonly made into the stick, lump, powder and more.) It has scaly crystal structure.

7N Antimony
Antimony is the metal element, symbol is Sb. Common Antimony is silver white, with hard and fragile character, and cold dilatant.

6N5 Antimony
Antimony is one gray metal, anti-acid material in the normal temperature, density is 6.68g/cm³, melting point is 630℃, fragile and non-extensive, is the poor conductor of electricity and heat, not easily to be oxidized, with anti- corrosion function.

6N Antimony
Antimony is to increase the hardness in the alloy, often called as the metal hardener. Antimony and its compound is firstly used in the Wear-resistant alloy, type alloy for printing, warheads for making bullets and shells in the military industry

5N Antimony
The amount of Antimony in the earth is 0.0001%, mainly existing in the single element or Stibnite, stibnite, antimonite and antimonite ochre.

4N Antimony
Antimony, atomic number 51, atomic weight 121.75, element name from the English name, originally meaning "stibnite". Antimony has been found in ancient times.

5N Germanium
Germanium is gray metalloid element, the chemical symbol is Ge, belonging to the group IVA of periodic table of elements. Germanium exists in the Zinc sulfide and certain sulfide ore, as one by-product acquired from the technology of Zinc smelting.

6N Bismuth
Bismuth has a series of excellent characteristics, such as high specific gravity, low melting point, volume expansion and contraction during solidification, etc.,

5N Bismuth
Crystalline, brittle metal, with reddish tinge. Soluble in nitric and hydrochloric acids. Highly diamagnetic (mass susceptibility -1.35 X 106). Expands 3.3% on solidification.

4N Bismuth
Bismuth is a metalloid element, with the element symbol Bi, belonging to the VIA group in the periodic table, atomic number 83, atomic mass 208.9804 g.mol -1. Bismuth has a melting point of 271 °C and a boiling point of 1420 °C .

6N Selenium
Selenium, element symbol Se, atomic number 34 in the periodic table, VIA group of non-metallic elements. Density is 4.809g/cm³, melting point 221 ℃, boiling point 685 ℃.

5N Selenium
Selenium, element symbol Se, atomic number 34 in the periodic table, VIA group of non-metallic elements. Density is 4.809g/cm³, melting point 221 ℃, boiling point 685 ℃.

3N5 Scandium
The element symbol is sc, the atomic number is 21, the atomic weight is 44.96, the peripheral electron arrangement is 3d14s2, and it is located in the fourth period IIIB group.

6N5 Aluminum
Aluminum is a metalloid element, with the element symbol Al, belonging to the VIA group in the periodic table, atomic number13, atomic mass 26.982 g.mol -1. Aluminum has a melting point of 660.323 °C and a boiling point of 2519 °C.
7N Tin
Tin is a silvery white glossy soft metal (square crystal system and cubic crystal system), with ductility. Melting point 231.88 ℃. Boiling point 2260 ℃.
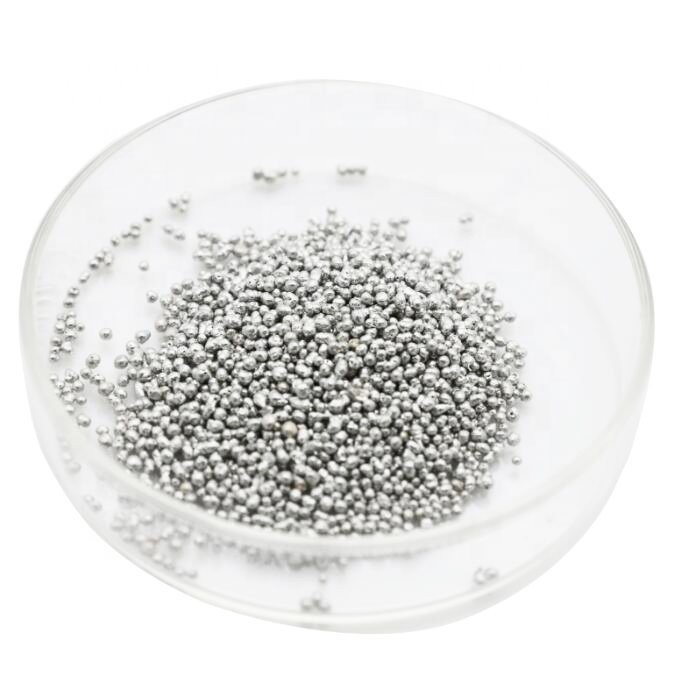

6N Tin
Tin is a silvery white glossy soft metal (square crystal system and cubic crystal system), with ductility. Melting point 231.88 ℃. Boiling point 2260 ℃.
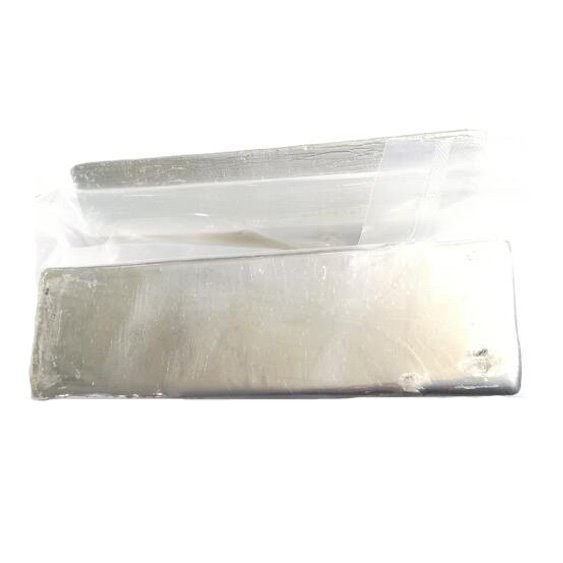

5N Tin
Tin is a silvery white glossy soft metal (square crystal system and cubic crystal system) with ductility. Melting point 231.88 ℃. Boiling point 2260 ℃.
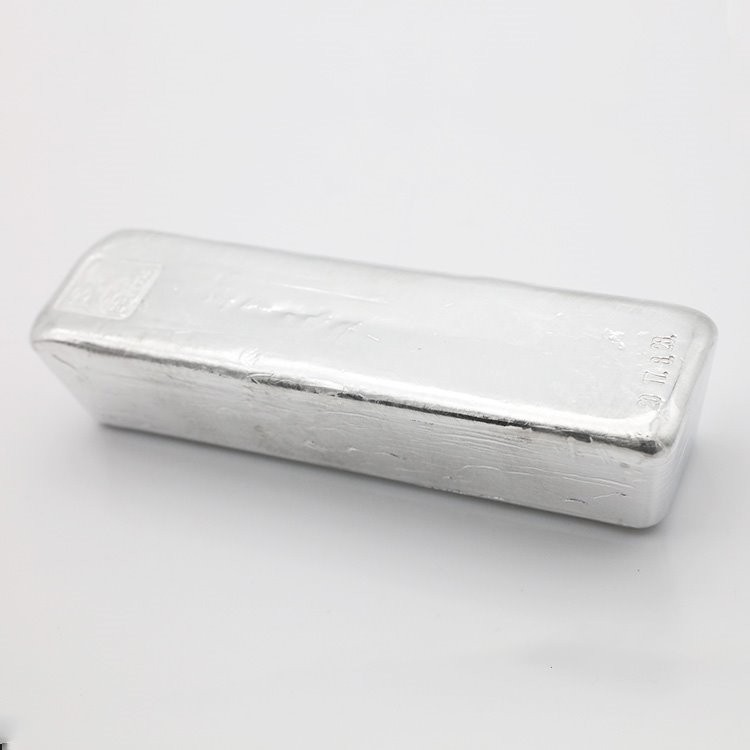

4N Tin
The chemical properties of tin are relatively stable. At room temperature, it hardly reacts with air. Atomic number 50, molecular weight: 118.710, density: 7.31 (α type), melting point: 231.85 (α type) ℃, boiling point: 2507 (α type) ℃.
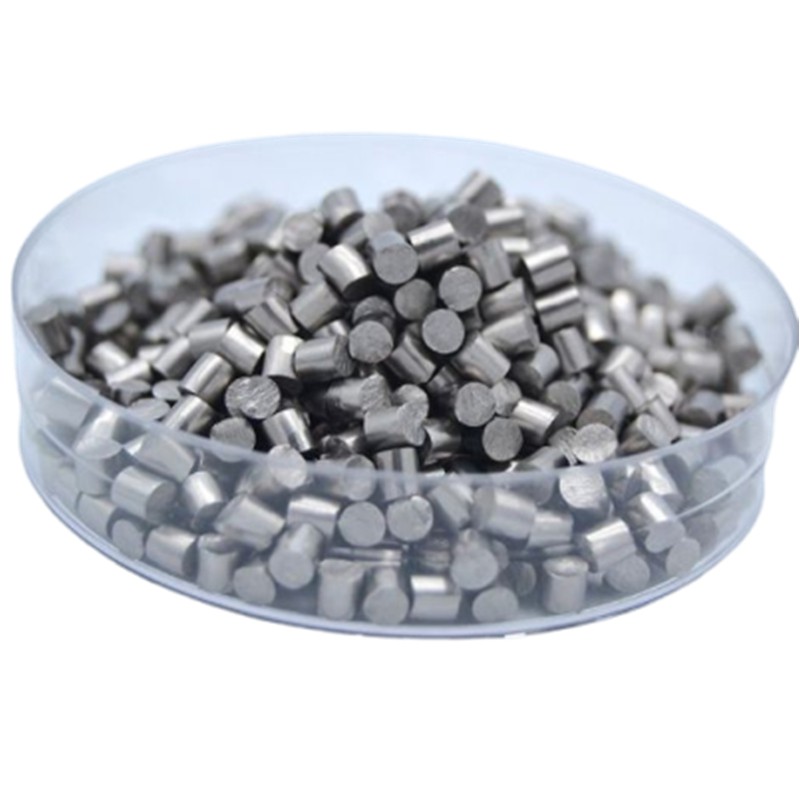

6N Zinc
Zinc is a metalloid element, atomic number 30, atomic mass 65.37 g.mol -1. Zinc has a melting point of 420 °C and a boiling point of 907 °C.
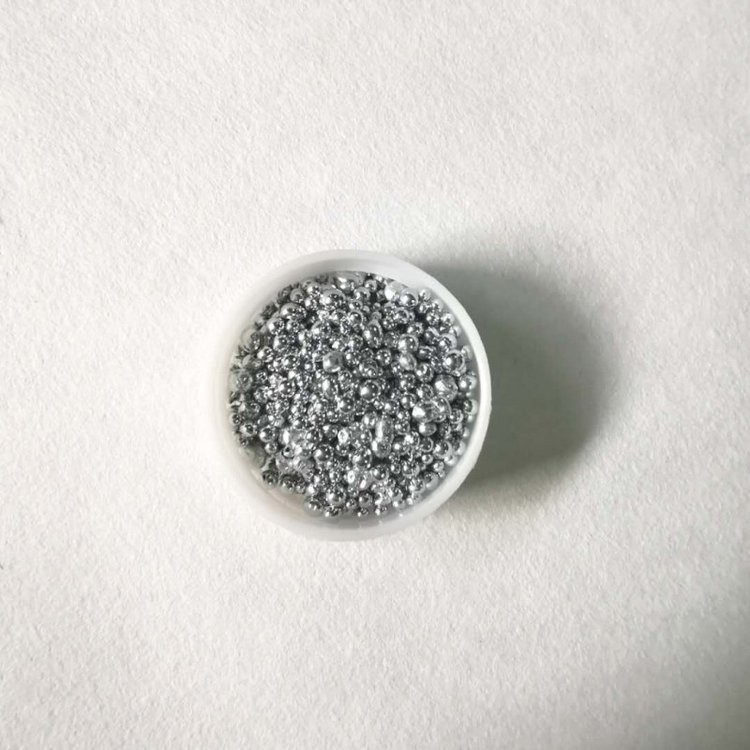

5N Zinc
Zinc is a metalloid element, with the element symbol Zn, belonging to the VIA group in the periodic table, atomic number 30, atomic mass 65.37 g.mol -1. Zinc has a melting point of 420 °C and a boiling point of 907 °C.

7N Arsenic
Arsenic, chemical element symbol as, atomic number 33. Melting point 817 ℃, boiling point 613 ℃, density 5.727 g / ml at 25 ℃. Gray metallic.
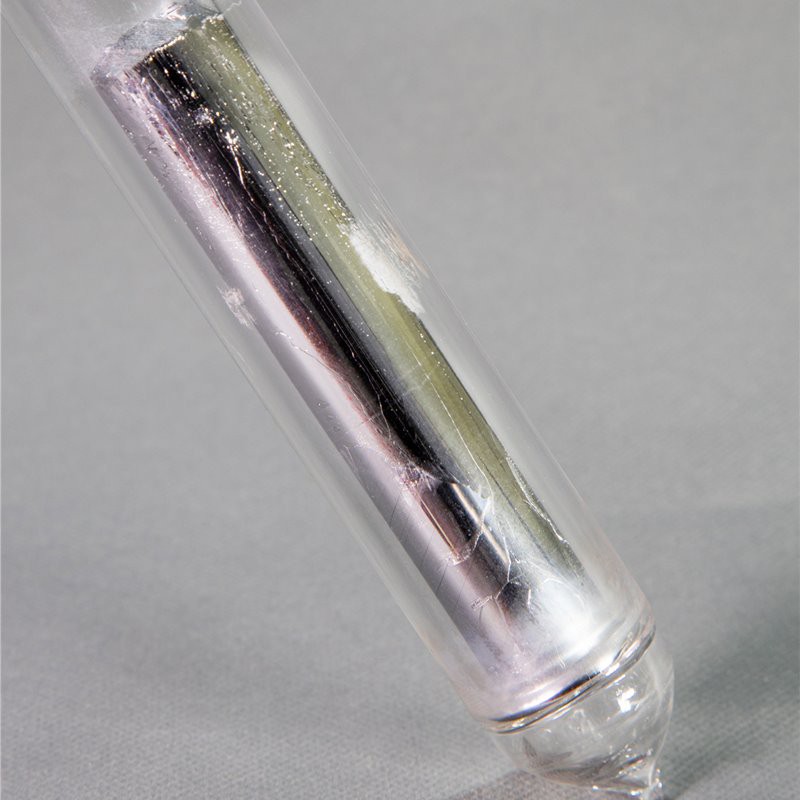

7N5 Arsenic
Arsenic, chemical element symbol as, atomic number 33. Melting point 817 °C, boiling point 613 °C, density 5.727 g / ml at 25 °C. Gray metallic. (α Type) is insoluble in water and soluble in nitric acid.
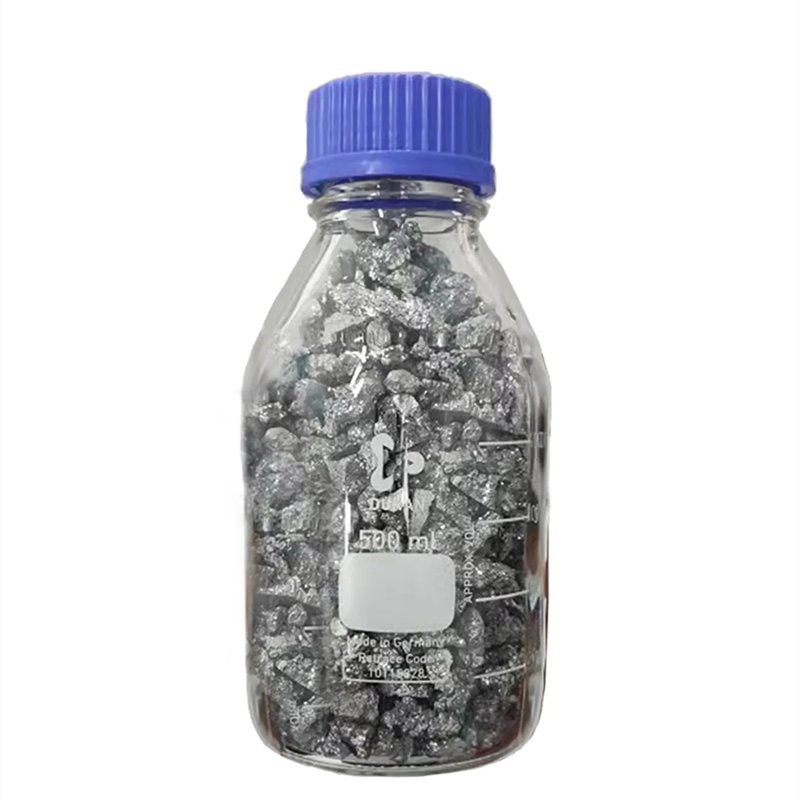

6N Arsenic
Arsenic is a silver-grey shiny block solid, hard and brittle. Vapor pressure 0.13kPa (372℃), melting point 817℃/3650kPa, boiling point 613℃, insoluble in water, lye, most organic solvents, soluble in nitric acid and hot lye, relative density 5.73g/cm³.
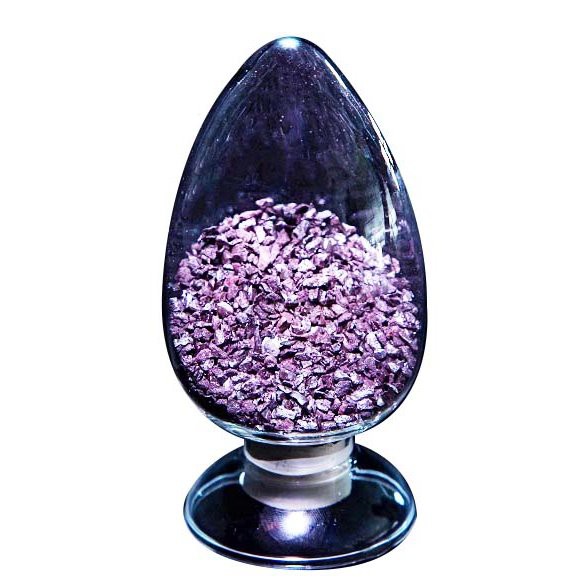

7N Red Phosphoras
Red phosphorus is the most common allotrope of phosphorus. It exists in an amorphous form and found to be more stable than white phosphorus.
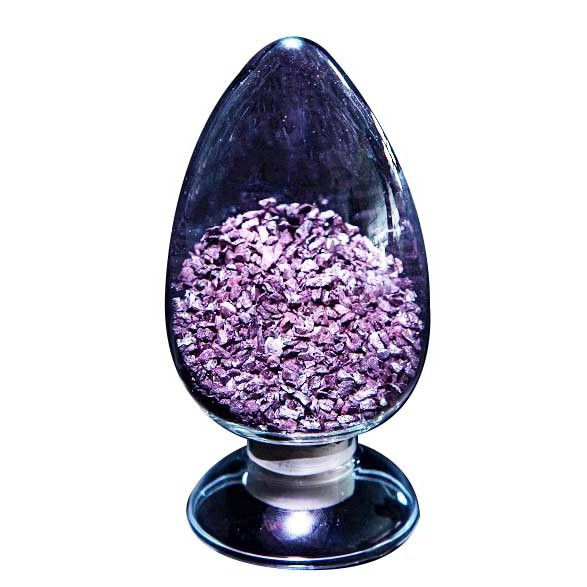

6N Red Phosphoras
Red phosphorus is located in the 15th position of the periodic table, the element symbol P. It is a purplish red or slightly brown amorphous powder with a luster.
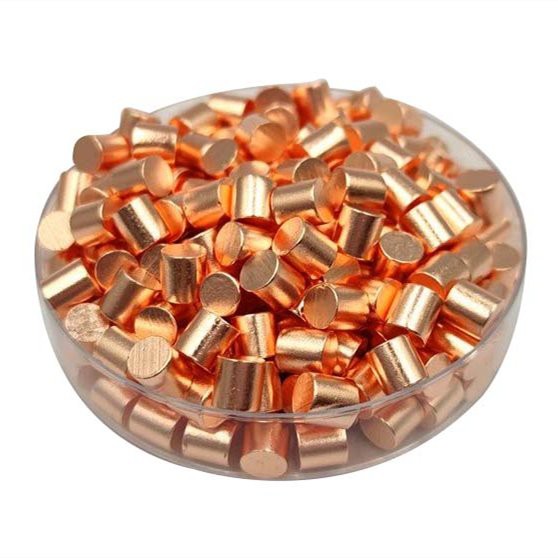

6N Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity.
